Manufacturing management software serves as a pivotal tool in the modern industrial landscape, streamlining processes and enhancing productivity. This software encompasses a range of functionalities designed to optimize manufacturing operations, from planning and scheduling to inventory management and quality control. By leveraging technology, organizations can significantly improve their efficiency and decision-making capabilities.
As the manufacturing sector evolves, the historical development of management software reflects a growing trend towards automation and data-driven decision-making. With advancements in technology, these solutions now integrate seamlessly with other systems, allowing for a holistic approach to manufacturing management.
Understanding the Basics of Manufacturing Management Software

Manufacturing management software is an essential tool that integrates various aspects of production and operation processes within the manufacturing industry. It streamlines tasks, enhances efficiency, and enables better decision-making by providing real-time data and insights. This software assists manufacturers in managing their resources effectively, ensuring that production runs smoothly and meets the demands of the market.Historically, manufacturing management software has evolved significantly from simple spreadsheet programs to sophisticated systems that incorporate advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning.
In the early days, manufacturers relied on manual processes and basic software applications, which were limited in functionality and scope. Over time, the rise of computerized systems led to the development of more comprehensive solutions that could handle inventory management, production scheduling, and quality control, among other functions.
Check hr software for small companies to inspect complete evaluations and testimonials from users.
Role of Technology in Modern Manufacturing Management Solutions
The role of technology in contemporary manufacturing management software is pivotal. It encompasses a range of innovations that enhance operational capabilities and provide strategic advantages. Here are some key technological elements that define modern manufacturing management solutions:
- Automation: Automation tools reduce the need for manual intervention, allowing for quicker production cycles and fewer errors. Robots and automated machinery can perform repetitive tasks, improving consistency and speed.
- Data Analytics: Advanced data analytics enable manufacturers to draw actionable insights from large volumes of data, facilitating informed decision-making and predictive maintenance.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud-based solutions offer flexibility and scalability, allowing manufacturers to access their systems from anywhere, ensuring that data is always available for analysis and operational management.
- Integration of IoT: The Internet of Things (IoT) connects machines and devices, providing real-time data that helps optimize operations and monitor equipment performance continuously.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI algorithms improve forecasting and inventory management, as they can analyze market trends and consumer behavior to adjust production schedules dynamically.
The integration of these technologies not only enhances the efficiency of manufacturing processes but also equips businesses to respond swiftly to market changes and customer demands. As manufacturers continue to embrace technological advancements, the landscape of manufacturing management software will likely evolve further, providing even more powerful tools for success in an increasingly competitive environment.
Key Features of Effective Manufacturing Management Software
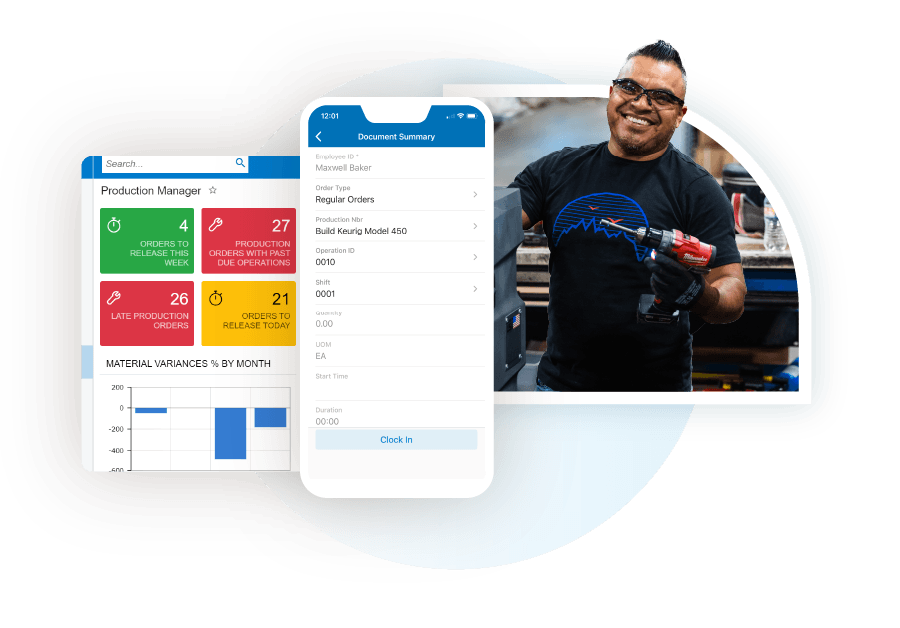
Effective manufacturing management software is essential for optimizing production processes, enhancing efficiency, and ensuring that operations run smoothly. The right software can transform how manufacturers manage their workflows, resources, and data. Understanding the key features of such software can help organizations select a tool that not only meets their current needs but also scales with them as they grow.One of the most critical aspects of manufacturing management software is its core features, which provide the backbone for streamlined operations.
These features not only automate tasks but also enhance visibility and collaboration across various departments. By leveraging these capabilities, manufacturers can reduce errors, save time, and improve overall productivity.
Essential Features of Manufacturing Management Software
When evaluating manufacturing management software, it is important to consider the following features, as they contribute significantly to operational efficiency:
- Inventory Management: This feature allows manufacturers to track raw materials and finished goods in real-time. By having a clear view of inventory levels, production schedules can be adjusted promptly to avoid shortages or overstock situations.
- Production Planning and Scheduling: Effective software should provide tools for planning and scheduling production runs. This ensures that resources are allocated efficiently, minimizing downtime and maximizing output.
- Quality Control Modules: Quality management features help in monitoring and maintaining product standards. They can include tools for inspection, testing, and compliance checks, which are crucial for meeting industry regulations.
- Data Analytics and Reporting: The ability to analyze production data and generate reports allows manufacturers to identify trends, make informed decisions, and implement continuous improvement strategies.
- Integration Capabilities: Manufacturing software should easily integrate with other systems such as ERP, CRM, and supply chain management tools. This connectivity enhances data flow across the organization and supports better decision-making.
User-friendly interfaces play a significant role in the overall effectiveness of manufacturing management software. A well-designed interface allows users to navigate the software intuitively, reducing the learning curve and minimizing errors during operation.
Importance of User-Friendly Interfaces
When users can easily interact with the software, they are more likely to utilize its full capabilities, which leads to increased efficiency and productivity. A user-friendly interface promotes engagement and ensures that employees at all levels can access the information they need without extensive training.Key aspects of user-friendly interfaces include:
- Intuitive Navigation: Clear menu structures and logical workflows enable users to find the features they need quickly.
- Customizable Dashboards: Personalized views allow users to prioritize the information most relevant to their roles, fostering quicker decision-making.
- Visual Data Representation: Graphs, charts, and other visual tools help users comprehend complex data sets and trends at a glance.
- Responsive Design: Compatibility with various devices, including smartphones and tablets, ensures that users can access critical information on the go.
Implementing manufacturing management software with these key features can significantly enhance a company’s production capabilities and overall efficiency. By focusing on user experience, manufacturers can empower their teams to leverage technology for better results.
Benefits of Implementing Manufacturing Management Software in Organizations
Manufacturing management software brings a multitude of advantages to organizations, significantly enhancing operational efficiency and effectiveness. As companies adapt to the evolving industrial landscape, leveraging technology in manufacturing processes becomes crucial for staying competitive and responsive to market demands. The integration of such software not only streamlines operations but also provides valuable insights that drive better decision-making.One of the foremost benefits of adopting manufacturing management software is its ability to improve operational efficiency.
By automating routine tasks, tracking production in real-time, and optimizing workflows, organizations can significantly reduce downtime and enhance productivity. This software facilitates better resource allocation, ensuring that materials and labor are utilized to their fullest potential. As a result, companies can achieve higher output levels while maintaining quality standards.
Impact on Cost Reduction and Resource Optimization
The implementation of manufacturing management software leads to substantial cost savings and improved resource optimization. By integrating different functionalities into a single platform, businesses can minimize waste, lower operational expenses, and improve inventory management. The software assists in identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies, allowing for timely interventions that further drive down costs. For instance, through predictive analytics, organizations can forecast demand more accurately and adjust their production schedules accordingly.
This not only prevents overproduction and excess inventory but also reduces storage costs and capital tied up in unsold products. The overall financial impact can be profound, with many companies reporting reductions in operational costs by as much as 15-30% after implementing manufacturing management software.
“Organizations can achieve higher output levels while maintaining quality standards.”
Enhancement of Decision-Making Processes
Manufacturing management software plays a crucial role in enhancing decision-making processes within organizations. By providing real-time data and analytics, this software empowers managers and teams to make informed choices based on accurate insights rather than gut feelings. The visibility offered by the software allows for better tracking of key performance indicators (KPIs) and trends, leading to more strategic planning and execution.Moreover, organizations can leverage data visualization tools within the software to interpret complex datasets easily.
For instance, a manufacturing company can utilize dashboards to monitor production rates, machinery performance, and labor efficiency simultaneously. This consolidated view enables quick assessments and faster responses to any issues that may arise on the shop floor.One notable example is a automotive manufacturer that adopted production management software, which allowed them to optimize their assembly lines. By analyzing data on workflow and machine performance, they were able to reduce lead times by 20%, directly impacting their ability to meet customer demands promptly.In conclusion, the benefits of implementing manufacturing management software are clear.
From enhancing operational efficiency to driving down costs and improving decision-making, organizations that harness the power of this technology can position themselves for success in today’s competitive manufacturing landscape.
Challenges in Adopting Manufacturing Management Software
Adopting manufacturing management software can significantly improve operational efficiency and productivity, but organizations often face several challenges during implementation. These challenges can stem from various factors including technology limitations, employee resistance, and integration issues with existing systems. Understanding these obstacles helps organizations formulate effective strategies to ensure a smoother transition and enhance overall user acceptance.One of the most prevalent challenges in implementing manufacturing management software is the resistance to change among employees.
This resistance often arises from a lack of understanding about the benefits of the software or fear of the unknown, leading to a reluctance to adapt to new processes. Another significant obstacle is the integration of the new software with legacy systems. Many organizations struggle to ensure compatibility between new solutions and existing hardware or software, which can lead to data silos and inefficiencies.
Understand how the union of hr management systems for small business can improve efficiency and productivity.
Common Obstacles in Implementation
The following Artikels common obstacles that organizations may encounter when adopting manufacturing management software:
- Employee Resistance: Employees may be hesitant to embrace new technologies due to fears of job displacement or discomfort with new systems.
- Integration Challenges: Legacy systems may not easily integrate with new software, creating compatibility issues that hinder operational efficiency.
- Data Migration Issues: Transferring data from old systems to new ones can be complex and fraught with errors if not managed properly.
- Training Deficiencies: Insufficient training may leave employees ill-equipped to effectively use the new software, leading to suboptimal utilization.
- Cost Implications: The initial investment in software and training can be substantial, which may deter organizations from moving forward.
Strategies to Overcome Challenges
To effectively address the challenges associated with adopting manufacturing management software, organizations can implement the following strategies:
- Change Management Planning: Establish a change management plan that emphasizes communication and transparency regarding the software’s benefits, which can help alleviate employee concerns.
- Comprehensive Training Programs: Develop thorough training programs that cater to different employee skill levels to ensure everyone feels confident using the new system.
- Incremental Implementation: Consider a phased approach to implementation that allows for gradual adoption and testing of the software, minimizing disruption to operations.
- Engagement of Key Stakeholders: Involve key stakeholders early in the process to foster buy-in and gather valuable feedback that can inform implementation strategies.
- Investing in Support Services: Partner with software vendors that provide robust support services to assist with integration and troubleshooting during the initial deployment phase.
Importance of Change Management
Change management plays a crucial role in the successful adoption of manufacturing management software. It ensures that all employees are not only aware of the forthcoming changes but are also prepared to embrace them. Effective change management includes providing clear communication about the reasons behind the software implementation and how it will benefit both the organization and its employees.
“Successful change management transforms resistance into acceptance, fostering a culture of continuous improvement.”
With a well-structured change management plan, organizations can significantly reduce resistance, enhance user engagement, and promote a positive attitude towards adopting new technologies, ultimately leading to a successful transition and maximized return on investment.
The Future of Manufacturing Management Software
The landscape of manufacturing management software is rapidly evolving, with new technologies and methodologies emerging to address the complexities of modern production environments. As industries strive for greater efficiency and adaptability, the role of software in managing manufacturing processes becomes increasingly pivotal. This section explores the trends shaping the future of manufacturing management software and the transformative potential of artificial intelligence and machine learning.
Emerging Trends in Manufacturing Management Software
The future of manufacturing management software is being influenced by several key trends that enhance functionality and improve operational efficiency. As organizations embrace digital transformation, the integration of advanced technologies is becoming essential.
- Cloud Computing: The shift towards cloud-based solutions enables manufacturers to access real-time data from anywhere, fostering collaboration and flexibility.
- IoT Integration: The Internet of Things (IoT) allows for the interconnection of machinery and devices, providing invaluable data for predictive maintenance and process optimization.
- Big Data Analytics: The ability to analyze vast amounts of data helps manufacturers make informed decisions, optimize supply chains, and forecast demand more accurately.
- Digital Twin Technology: Creating digital replicas of physical systems enables manufacturers to simulate and optimize processes before implementation.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning on Manufacturing Processes, Manufacturing management software
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are poised to revolutionize manufacturing processes by enhancing automation and decision-making capabilities. These technologies can analyze historical data and identify patterns, leading to smarter manufacturing practices.
AI-driven systems can reduce downtime by predicting equipment failures before they occur, thus minimizing unplanned disruptions.
Applications of AI and ML in manufacturing include:
- Predictive Maintenance: AI algorithms can forecast when machinery is likely to fail, allowing for timely maintenance that prevents costly downtime.
- Quality Control: Machine learning models can analyze production quality in real-time and adjust processes to maintain high standards.
- Supply Chain Optimization: AI can enhance inventory management by predicting demand trends and optimizing stock levels accordingly.
Future Developments Reshaping Manufacturing Management Strategies
Future developments in manufacturing management software will fundamentally reshape strategies, making them more responsive to market changes and customer needs. As manufacturers adopt more intelligent systems, the focus will shift toward agility and customization.
- Personalized Production: The rise of mass customization will enable manufacturers to tailor products to individual customer specifications without sacrificing efficiency.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Software solutions will increasingly incorporate tools for tracking and reducing carbon footprints, promoting environmentally friendly practices.
- Enhanced Collaboration Tools: Future software will likely feature improved collaboration platforms, allowing teams to work together seamlessly across different locations.
- Integration with Blockchain: Blockchain technology can enhance transparency and traceability in supply chains, fostering trust among stakeholders.
Evaluating Different Manufacturing Management Software Solutions
Choosing the right manufacturing management software is a critical decision for any organization looking to enhance productivity and streamline operations. With a myriad of options available, it’s essential to evaluate each one against specific criteria to ensure it meets the unique needs of your business. This section delves into the various software solutions on the market, highlights the factors to consider during selection, and analyzes customer reviews and case studies of popular software.
Comparison of Manufacturing Management Software Options
Several manufacturing management software solutions stand out in the market due to their features, usability, and customer satisfaction. Understanding the differences can help organizations make informed choices. Here’s a comparison of some leading options:
- Prodsmart: Ideal for small to medium-sized businesses, Prodsmart offers real-time data collection and analytics, emphasizing lean manufacturing principles.
- Fishbowl Manufacturing: This solution integrates seamlessly with QuickBooks, providing efficient inventory management alongside manufacturing capabilities, making it suitable for various industries.
- Odoo: Known for its modularity, Odoo allows businesses to tailor their systems by choosing the modules that fit their needs best, covering everything from manufacturing to CRM.
- Plex: Designed for the manufacturing sector, Plex focuses on cloud-based solutions that provide comprehensive visibility and control over production processes.
- Syteline (Infor CloudSuite): This is a robust solution for larger enterprises, offering extensive customization and advanced analytics tailored to complex manufacturing environments.
Criteria for Selecting Manufacturing Management Software
When evaluating manufacturing management software, several key criteria should guide your decision-making process. Each criterion contributes to the overall effectiveness and efficiency of the software in meeting your organization’s goals.
- Scalability: The software should accommodate growth and adapt to changing business needs.
- Usability: An intuitive user interface is crucial for ensuring that employees can quickly learn and effectively use the system.
- Integration: The ability to integrate with existing systems, such as ERP and accounting software, enhances functionality and streamlines operations.
- Support and Training: Look for vendors that offer robust customer support and training programs to assist with implementation and ongoing use.
- Cost: Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including licensing, maintenance, and hidden costs, to ensure the software fits within your budget.
Analysis of Customer Reviews and Case Studies
Analyzing customer reviews and case studies provides valuable insights into the real-world performance and user satisfaction of manufacturing management software. Here are some key takeaways drawn from user experiences:
“Prodsmart helped us reduce our production time by 30%, allowing for a quicker response to market demands.”
A small manufacturer in the electronics industry.
“Fishbowl’s integration with QuickBooks was a game-changer for us, simplifying our inventory management and accounting processes.”
Learn about more about the process of best hr software for startups in the field.
A mid-sized furniture manufacturer.
Case studies reveal that organizations that prioritize training and user adoption alongside software implementation tend to achieve greater success rates. For instance, a case study from a large automotive parts manufacturer showed that thorough training on Plex resulted in a 45% increase in production efficiency within the first year of use.By considering these comparisons, criteria, and real-world examples, organizations can make more informed decisions when selecting manufacturing management software that aligns with their operational needs and enhances overall performance.
Integrating Manufacturing Management Software with Other Systems
The integration of manufacturing management software with other critical business systems, such as supply chain management and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, is essential for creating a cohesive operational environment. This integration fosters enhanced communication and data sharing, streamlining processes across various departments. By ensuring that manufacturing management software collaborates seamlessly with existing systems, organizations can leverage real-time data to make informed decisions, ultimately improving productivity and efficiency.Integrating manufacturing management software with supply chain and ERP systems allows organizations to synchronize production schedules, inventory levels, and customer demand.
This alignment is crucial for maintaining optimal operational efficiency and ensuring that resources are utilized effectively. For instance, when manufacturing software is connected to an ERP system, it can automatically adjust production plans in response to changes in demand or supply chain disruptions. This responsiveness reduces lead times and enhances overall agility in manufacturing processes.
Benefits of Seamless Data Exchange
Seamless data exchange between manufacturing management software, supply chain systems, and ERP platforms is vital for achieving a unified view of business operations. Here are some key benefits that arise from this integration:
- Enhanced Visibility: Real-time data sharing allows stakeholders to monitor inventories, production schedules, and order statuses, facilitating better decision-making across the organization.
- Improved Collaboration: Departments can work together more effectively, as integrated systems eliminate data silos and promote cross-functional communication.
- Reduced Errors: Automatic data transfer minimizes the risk of human error associated with manual data entry, ensuring higher data accuracy and reliability.
- Increased Efficiency: Streamlined processes lead to quicker response times and reduced bottlenecks, resulting in a more agile manufacturing operation.
- Data-Driven Insights: With comprehensive data from all systems, organizations can analyze performance metrics, identify trends, and make strategic decisions based on empirical evidence.
Best Practices for Successful Integration
Ensuring successful integration of manufacturing management software with other systems requires careful planning and execution. Here are some best practices that organizations should consider:
- Define Clear Objectives: Establishing specific goals for integration helps in aligning efforts and measuring success throughout the process.
- Choose the Right Technology: Selecting compatible software and tools that can communicate effectively with existing systems is crucial for smooth integration.
- Involve Stakeholders: Engaging key stakeholders from various departments early in the integration process can provide valuable insights and foster buy-in.
- Prioritize Data Quality: Ensuring high-quality, clean data is fundamental to the success of integration efforts, as inaccurate data can lead to poor decision-making.
- Monitor and Adjust: Continuous monitoring of the integration process allows organizations to identify issues and make necessary adjustments to optimize performance.
Integrating manufacturing management software with supply chain and ERP systems is not just a technical necessity; it is a strategic imperative that positions organizations for success in a competitive landscape. By embracing these integrations, companies can enhance operational efficiency, improve collaboration, and leverage data for informed decision-making.
The Role of Training in Utilizing Manufacturing Management Software
Training programs play a crucial role in maximizing the benefits of manufacturing management software. As organizations increasingly adopt these tools to streamline operations and improve efficiency, ensuring employees are well-trained is essential for effective usage. Proper training helps to minimize errors, boosts productivity, and enhances user confidence, leading to a smoother transition and better overall results.To facilitate successful adoption of manufacturing management software, various training methods can be employed, each with its own strengths in helping employees become proficient users.
Effective training not only covers the technical aspects of the software but also emphasizes the importance of integrating this technology into daily workflows.
Different Training Methods and Their Effectiveness
The choice of training methods can significantly impact how well employees adapt to manufacturing management software. Here are some common training methods along with their effectiveness:
- Classroom Training: This traditional method provides structured learning and allows for direct interaction with the instructor. Employees can ask questions and engage in discussions, which enhances understanding.
- Online Training: Flexible and accessible, online training allows employees to learn at their own pace. Many organizations utilize webinars and e-learning modules that can be revisited as needed, making this method popular.
- Hands-On Training: Practical sessions where employees can use the software in real-world scenarios are invaluable. This method fosters experiential learning, enabling users to troubleshoot and solve problems in real time.
- Peer-to-Peer Training: Utilizing experienced employees to mentor and train their colleagues can be effective. This approach fosters a collaborative learning environment and allows for sharing best practices specific to the organization’s processes.
- Vendor-Specific Training: Many software vendors offer tailored training sessions for their products. These sessions are particularly beneficial since they cover features and functionalities specific to the software, ensuring comprehensive understanding.
Implementing a combination of these methods can provide a well-rounded training program that caters to diverse learning styles within the workforce.
Examples of Successful Training Implementations
Several manufacturing organizations have achieved success through effective training implementations for their manufacturing management software. For instance, a leading automotive manufacturer introduced an extensive training program that combined online and hands-on training sessions. Employees were first required to complete online modules before attending hands-on workshops, resulting in a significant increase in the software’s adoption rate and overall productivity.Another example can be seen in a mid-sized electronics manufacturer that opted for a peer-to-peer training approach, allowing its most technically adept employees to guide their colleagues.
This not only empowered the experienced users but also built a sense of teamwork and camaraderie, leading to quicker proficiency across the team. In both cases, the emphasis was on continuous learning, where follow-up sessions and refresher courses were offered to ensure that employees remained updated with any software upgrades or new functionalities. By prioritizing training, these organizations were able to realize the full potential of their manufacturing management software, enhancing their operational efficiency and competitiveness in the market.
Final Review
In conclusion, the implementation of manufacturing management software not only addresses operational challenges but also paves the way for future innovations within the industry. As organizations navigate the complexities of manufacturing, embracing these solutions can lead to enhanced efficiency, reduced costs, and improved decision-making. The future of manufacturing management software looks promising, with technology continuing to revolutionize how industries operate.
FAQ Explained: Manufacturing Management Software
What is manufacturing management software?
Manufacturing management software is a tool designed to streamline and optimize manufacturing processes, including planning, scheduling, and inventory management.
How can manufacturing management software improve efficiency?
It enhances efficiency by automating processes, reducing errors, and providing real-time data for better decision-making.
What are the common challenges in adopting this software?
Common challenges include resistance to change, integration issues with existing systems, and the need for comprehensive training.
What features should I look for in manufacturing management software?
Key features include user-friendly interfaces, real-time data analytics, integration capabilities, and flexibility to adapt to different manufacturing processes.
How does training impact the use of manufacturing management software?
Effective training is crucial for successful adoption, ensuring that employees can utilize the software to its full potential for enhanced productivity.